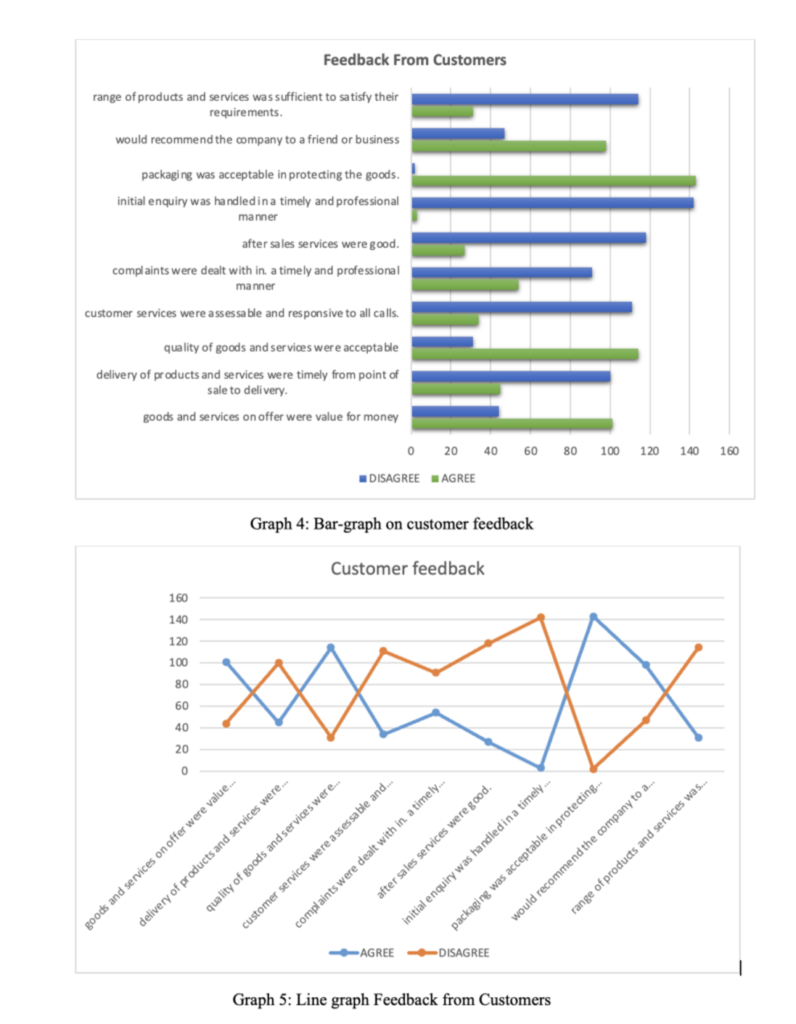
Task One
Articles
Introduction
Decision making is critical for an organisations perfomance . There are is a wide range of decision -making approaches that could be used to identify possible solutions to organisational problems as well as specific issues relating to people practice.Evidence based practice is one of the concepts of decision making that has proven to give the desired outcome.It is based on the concept that good decision making is attained through drawing on the best available evidence and critical thinking(CIPD, 2020). Evidence based practice is governed by several principles such as critical thinking. There are various theories that are linked to this approach and are of significance to decision making eg Utilitarianism ethical theory and Kant’s moral theory .
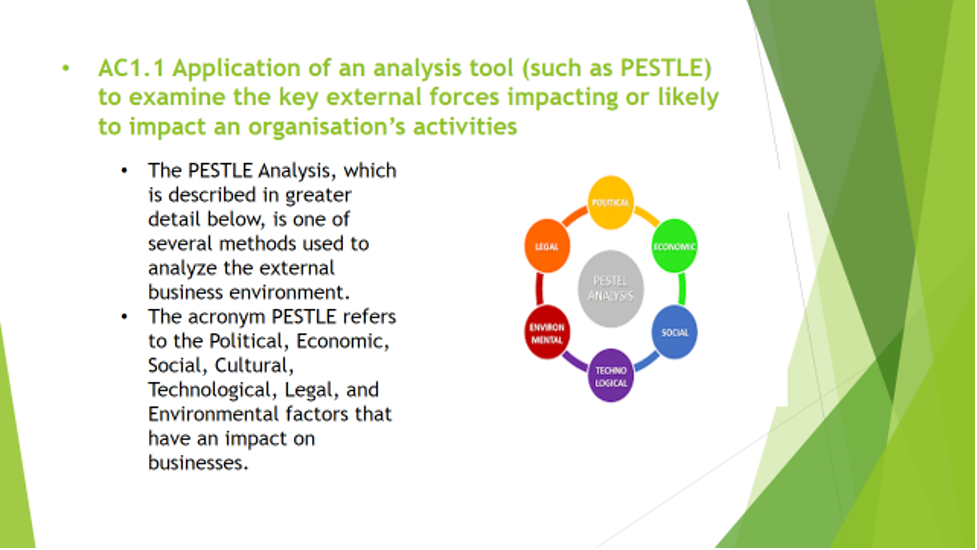
AC 1.2 Evaluate Micro-and Macro-Analysis Tools that can be used in Human Resource practice to Investigate an Organisation's Micro and Macro Environment and How those Discovered can be used to Diagnose Future Issues, Challenges, and Opportunities.
Internal and external factors affect every organisation. These aspects are all part of the broader organisational environment, and their effects on the firm should be evaluated. In people practice, various tools are employed, including strategy reviews, future state analyses, SWOT analyses, Ansoff matrix analyses, and Fishbone analyses.There are various ways to evaluate an organisation’s micro and macro environments, they include : Observations, interviews, job analysis, work sampling, and the use of questionnaires.
The micro-environment of an organisation refers to the primary factors or environment in which it operates. These elements or environments include suppliers, consumers, competitors, and stakeholders (Summer, 2019). These are internal factors that can have an effect on an organisation. Microenvironments can be evaluated using microanalysis methodologies such as Porter’s five forces analysis. On the other hand, the macro-environment refers to the broader forces that affect enterprises (Summer, 2019). Macro-environments are external elements that have an effect on an organisation’s activities and production but are beyond its control. Economic difficulties, political forces, technical breakthroughs, ecological and physical phenomena, and legal factors contribute to the macroenvironment. The PESTLE analysis tool is an illustration of a tool used to analyse macro-environmental factors.
The SWOT analysis tool assesses both internal and external issues affecting an organisation. SWOT analysis is a strategic planning technique that identifies a company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (Summer, 2019). While strengths and weaknesses are concerned with the organisation’s internal workings, threats and opportunities are concerned with external issues that may affect the organisation. The SWOT analysis is a straightforward process that can be utilised by businesses entering new markets.
Michael Porter developed Porter’s five analysis method for assessing and evaluating a business’s competitive strength (Bruijl, 2018). The approach is based on five concepts and can be used to evaluate an organisation’s microenvironment. Porter identified five forces: negotiating power of buyers, the threat of entrance, bargaining power of suppliers, competition from rivals, and threats from replacements.
As the acronym implies, the PESTLE study examines political, economic, social, technical, legal, and environmental concerns (Downey, 2007). Political variables such as trade restrictions and policies and diplomatic difficulties are likely to affect an organisation’s performance. It is critical to note that organisations are governed by laws and regulations developed by trade unions and other regulating agencies in the UK. As a result, the human resources department is responsible for ensuring that the organisation adheres to all applicable requirements. Additionally, human resources should be kept up to date on regulatory developments that may affect an organisation.
The state of the economy is a significant external factor influencing any firm. Human resources should monitor changes in economic trends as a result of global financial instability. Organisations are directly affected by economic issues such as inflation, demand and supply, interest rates, and currency exchange rates (Friedman, 2013). Human resources should inform management of current economic trends in order to prepare them for future developments. The availability of a workforce can affect an organisation’s effectiveness on a social level. Human resources are accountable for developing a recruiting strategy that attracts the finest personnel to perform organisational functions. Technological factors include the influence of adopting new technology, which may need personnel reductions or recruitment. Human resources are responsible for advising management on essential modifications to ensure that technological advancements benefit the organisation and that the organisation retains a technologically savvy staff (Friedman, 2013).
Legal aspects include rules and regulations that affect how individuals conduct themselves. Human resource professionals should ensure that the organisation and its existing policies and procedures adhere to all applicable regulatory standards in the country (Friedman, 2013). The final ‘E’ in the PESTLE tool stands for environmental elements, which allude to a naturally occurring element that may affect how individuals behave. Global market forces are compelled to comply with sustainable development goals. The Human Resources department’s responsibility is to guarantee that the organisation complies with all applicable laws and incorporates environmental sustainability policies into daily operations.
AC 1.1 Assesses the notion of Evidence-Based Practice.
Evidence based practice is based on the concept that good decision making is attained through drawing on the best available evidence and critical thinking(CIPD, 2020).It entails use of verifiable basis to find solutions to dealing with people management The decisison is evaluated against available data in an organisation..Evidence based decisions tend to yield the desired outcome that impacts an organisations practise. The evidence-based approach makes use of critical thinking abilities and accessible evidence to make decisions about specific human resource concerns. According to Young (2020), sound decision-making requires critical thinking and a careful examination of the available data.
Additionally, evidence-based practice makes use of alternative decision-making models, such as the rational model. This paradigm entails the application of factual data and gradual procedures to arrive at a decision (Uzonwanne, 2016). The summary of the rational decision-making model is shown in the diagram below.
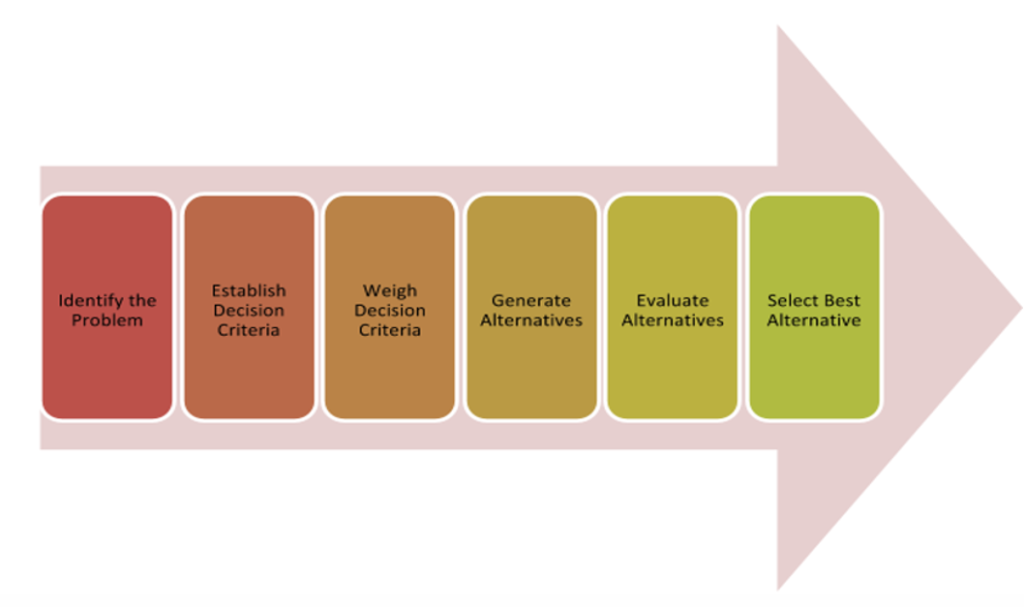
Figure 1: Rational Decision-Making Model (Lumenlearning.com, 2019)
How evidence-based approaches can be used to aid in the development of sound judgments and decision-making
Evidence-based techniques are essential for aiding sound decision making since they reduce the likelihood of making erroneous judgments. In the lack of evidence, it is reasonable to predict unreasonable and unreliable managerial judgments. Managers are prone to bias and inaccuracy when making judgments based on their prior experiences or popular management methods, and this is especially true for senior executives. As stated in an article published by the Center for Evidence-Based Management (CEBM), all employees at all levels of the organisation must make decisions based on the best available evidence. According to Uzonwanne (2016), making decisions on the basis of evidence is deemed morally correct.
It is possible to utilise an evidence-based approach to enhance effective decision making and judgement by raising responsibility at the organisational level and by increasing transparency. The vast majority of managerial decisions have an impact on the overall performance of the organisation, whether in a positive or negative way. Evidence that has had reliability and validity checked has a positive impact on both individuals and organisations. It is through this technique that a manager can make the best decision feasible, which can be supported by organisational data, professional expertise, or findings from scientific study.
AC 1.4 At least two distinct ethical theories and views should be considered in decision making.
Utilitarianism is an ethical philosophy that focuses on the outcome in order to define what is right and wrong (Driver, 2009). It is one of the most frequently used persuasive tactics in the subject of normative ethics, and it is also one of the most effective. A choice that is most ethical is defined as one that results in the greatest amount of good, according to this viewpoint. It is possible to use this concept to inform and influence excellent decision making when the decision is in the best interests of the majority of employees or the organisation as a whole. As an example, the Covid 19 pandemic has impacted countless organisations, prompting the deployment of low-wage labour to compensate for the damage. In this situation, human resource professionals must choose between laying off employees and hiring new staff at a cheaper cost. Despite the fact that this is unethical, it will improve the long-term viability of organisations, particularly those that have been impacted by the pandemic. Justice, as well as any sense of individual rights, are excluded from this worldview.
Kantianism, often known as Kant’s moral theory, on the other hand, maintains that specific actions are prohibited regardless of the outcome. It is a deontological moral theory in which the focus is placed on an individual’s moral obligation rather than the outcome of a particular action or inaction (Chonko, 2012). Individuals’ ability to act morally in accordance with universal categorical imperatives is founded on the principle of moral responsibility. As a result of this concept, decisions should be made in light of an individual or a society’s moral and ethical duties. Because of this, the decision will be ethical (Chonko, 2012).
Influence of Theories in decision making.
A lot of what people think about when they make decisions has an impact on how they make decisions. In order to make good ethical decisions, you need to pay attention to what you do. HR should be in charge of most of an organization’s ethical responsibilities, even though the theories are broken up into three frameworks. Concomitantist: This is a type of ethical framework that is based on ethical theories. Duty: This is a type of ethical framework based on ethical theories. Virtue: Using the three frameworks to think about a situation before making a decision helps the person who makes the decision have a clearer picture of the matter at hand and come up with a sound decision that takes into account the ethical implications and the people who are involved (Bonde and Firenze, 2011). In the figure below, you can see a summary of different ethical theories, as well as their benefits and drawbacks.
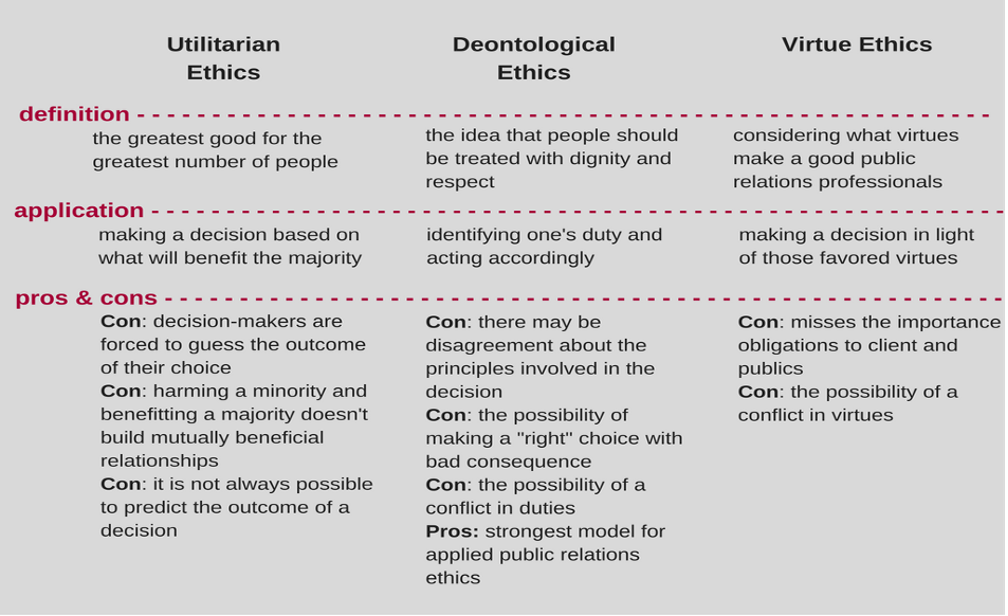
Ethical Theories, Illustration 3 (Source: www.pagecentertraining.psu.edu, 2020)
AC 1.3. Discuss critical thinking principles and provide instances of how you apply them to your own and others’ ideas in order to facilitate objective and rational discourse.
The ability to think critically is a skill that helps people make good decisions and think about ideas, opinions, and arguments in a clear way (Howlett and Coburn, 2019). To make a decision, you have to look at people’s practise issues objectively and make a decision. Many critical thinking principles are based on rational, objective analysis of factual information and sceptical analysis, which is what the definition says. Being logically correct is what objective, rational thinking is all about. This principle lets you separate things that are true from things that aren’t. Walters says that rational, objective thinking is based on logic and other cognitive acts like imagination, creativity, and ideas.
In real life, people can use different critical thinking principles in different situations. When HR professionals use critical thinking to make decisions, they need to make sure they understand the issue and can tell the difference between facts and opinions(Howlett and Coburn, 2019). When making decisions based on evidence, you use the critical thinking principle of valid evidence to remove any bias.
AC 2.3 Describe various decision-making strategies that could be utilised to explore potential solutions to a particular challenge in human resource practice.
Human resource professionals are crucial in an organisation’s decision-making process. The HRM has several decision-making processes they can utilise to uncover probable answers to specific challenges depending on the functions of human resource practitioners. Human resource professionals employ various decision-making techniques, including best fit, future pacing, problem-outcome framing, action learning methodologies, and de Bono selection (Six Thinking hats). While a single procedure can be utilised to address various human resource concerns, different situations may necessitate a distinct approach to decision-making.
Edward De Bono invented De Bono (six thinking caps) in 1985 as a decision-making approach. Because it comprises a combined parallel process, it is an effective decision-making strategy for group debates and personal reflection. Each of the six hats represents one of the six distinct modes of thought. By mentally donning several thinking hats, individuals can approach problems differently and provide novel solutions—the six distinct mind frames described by Edwards are represented by various forms and colours of the hat. The white colour is symbolic of fact-based judgments. The colour red is associated with emotional decisions. Black denotes judging decisions, yellow denotes a favourable outlook or decisions made from a positive perspective, green denotes creative choices, and blue denotes reflective decisions (Mulder, 2019). Managers and human resource professionals can wear multiple hats during the decision-making process. The thinking caps are critical in assisting individuals in delving deeper into certain situations and making educated choices.
Framing challenges and outcomes is another decision-making technique that may be used to explore potential solutions to individual problems. Framing is a collection of interpretations on which various individuals rely in order to comprehend and respond to events. Different diagnoses and framings of issues might create complications when attempting to resolve them. Human resource practitioners must appropriately frame their organisation’s concerns to obtain the intended outcome. For instance, depending on how turnover is judged, it may be portrayed as an individual, human resources, or management issue.
AC 2.4 provide a rationale for your decision, having used one or more decision-making tools to determine a recommended course of action based on evaluation of the benefits, risks and financial implications of potential solutions
People practise involves ongoing decision-making during an employee’s tenure with the organisation. Compensation is one area of human conduct that necessitates sound judgement. Increased employee remuneration is a deliberate decision, as various circumstances influence it. While performance analysis is critical for compensation determination, it should also address other elements such as the minimum wage, external markets, and industrial payment rates.
Attracting and maintaining talent is a people-intensive process that can present various difficulties. Governmental and private companies face intense competition for the most skilled and qualified people. Recruitment of a sustainable staff is critical to the effectiveness and sustainability of an organisation. On the other hand, competitive pay and benefits may have an effect on turnover and the evaporation of the finest talent pool. The human resources department is responsible for making difficult decisions regarding the most effective strategies for increasing retention and recruiting the most outstanding talent pool. The framing-outcomes decision-making approach can be used to address retention and recruitment issues. Human resources can pinpoint particular reasons for turnover, ranging from compensation and benefits to organisational culture and the desire for professional advancement. HR can develop a solution that results in the desired outcome by defining the cause of the problem.
AC 3.1 Evaluate organisations' financial and non-financial performance measurement methods.
In order to achieve success in business, proper performance management is required (Gifford, 2020). In order to ensure that employee performance is aligned with organisational goals, performance management attempts to monitor, maintain, and improve employee performance while also ensuring that it is improved. Organizations, on the other hand, can evaluate their own success in a variety of ways. Because it is a component of evidence-based people management techniques, performance monitoring is essential for decision-making.
Financial and non-financial measures can both be used to evaluate the performance of an organization’s operations. Indicators of financial performance include revenues, gross and net profits, cash flows, the rate of return on investment, and productivity, to name a few. Profitability ratios such as gross and net profit margins are used to determine a business’s profitability. Work in progress capital (WK) is a statistic that reflects the amount of readily available operating liquidity that is used to fund routine business operations. When a business creates money from its operations, it is measured by cash flow, which is a financial statistic in itself. A cash flow statement that includes an operating cash flow is commonly seen.
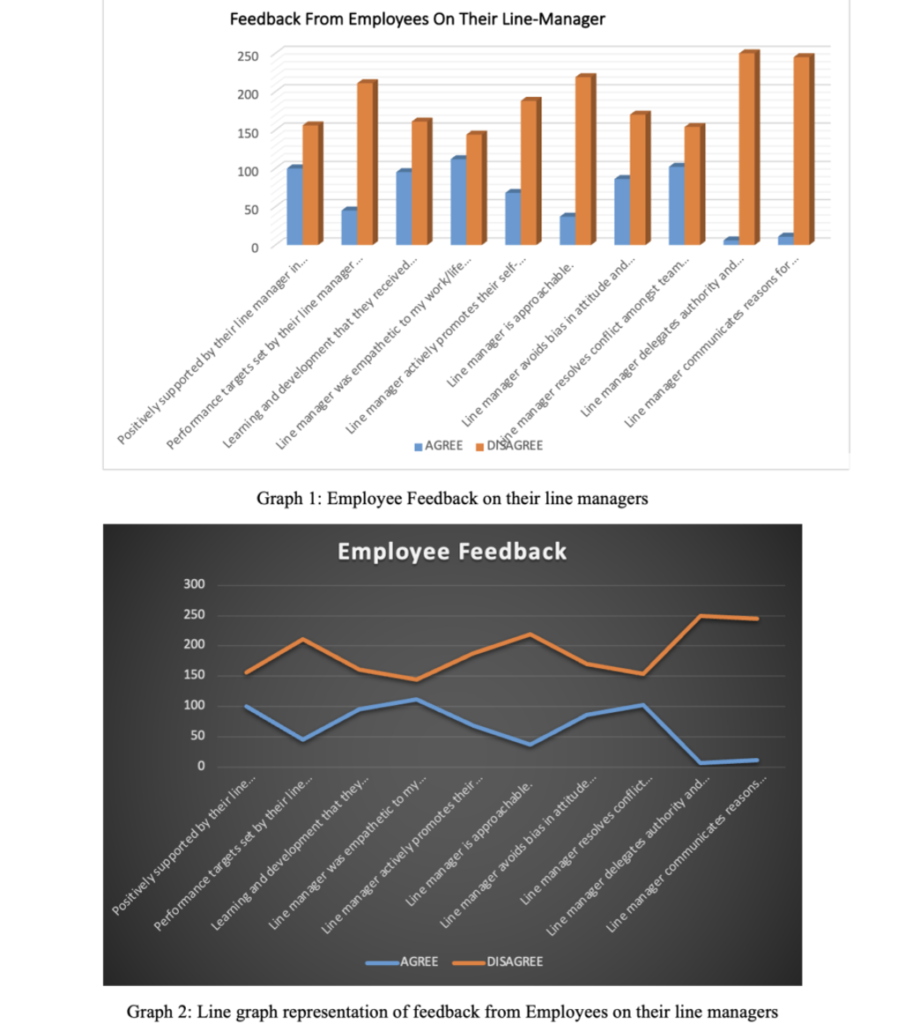
The following are examples of non-financial performance indicators: customer feedback, sector ratings, legal compliance, staff feedback, and other non-financial performance indicators. Because they have a direct impact on how long customers remain with a company, customer feedback and customer retention are key non-financial success measures. Client retention is just as crucial as customer attraction in terms of business success. When it comes to determining how many consumers are satisfied with a product or service, customer retention is critical, and feedback helps an organisation figure out how to improve. A company’s human capital can also be utilised to determine how well it is performing. Based on the results of the survey, an organisation can determine how well it is performing by comparing the number of talented employees it has to the number of unqualified employees it has.
The most important advantage of non-financial indicators is that they lead to stronger alignment with the long-term corporate strategy of the organisation. A large number of intangible assets are represented by non-monetary indicators, which provide sufficient information on the effectiveness of various operations (Ahrens and Chapman, 2007). Among the disadvantages of non-monetary solutions include the fact that they are time-consuming and costly to implement. In addition to being exact and easily monitorable, financial measures offer the advantage of being transparent. As a drawback, because they are primarily concerned with the short term, they are ineffective for long-term strategic planning.
References
Bonde, S. and Firenze, P. (2011) A Framework for Making Ethical Decisions | Science and Technology Studies. [online] Brown University. Available at: https://www.brown.edu/academics/science-and-technology-studies/framework-making-ethical-decisions .
Brugman, T. and Dijk, R. van (2020) Creating Value With Fact-Based HR. [online] AIHR Analytics. Available at: https://www.analyticsinhr.com/blog/creating-value-fact-based-hr/.
Bruijl, G.H.Th. (2018) The Relevance of Porter’s Five Forces in Today’s Innovative and Changing Business Environment. SSRN Electronic Journal, [online] 1(1). Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326026986_The_Relevance_of_Porter’s_Five_Forces_in_Today’s_Innovative_and_Changing_Business_Environment [Accessed 9 Apr. 2021].
Chonko, L. (2012). Ethical Theories. [online] . Available at: https://www.dsef.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/EthicalTheories.pdf.
CIPD (2020) People Data & Scientific Evidence. [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/analytics#gref .
Downey, J. (2007) Strategic Analysis Tools Topic Gateway Series Strategic Analysis Tools Topic Gateway Series No. 34. [online] . Available at: https://www.cimaglobal.com/Documents/ImportedDocuments/cid_tg_strategic_analysis_tools_nov07.pdf.pdf .
Driver, J. (2009) The History of Utilitarianism. [online] Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Available at: https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/utilitarianism-history/ .
Friedman, E. (2019) 4 External Factors That Affect Human Resource Management. [online] Workology. Available at: https://workology.com/4-external-factors-that-affect-human-resource-management/.
Gifford, J. (2020) Performance Management | Factsheets. [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/people/performance/factsheet#gref .
Hayes, A. and Anderson, S. (2021) Cost Benefit Analysis | Better Evaluation. [online] Betterevaluation.org. Available at: https://www.betterevaluation.org/en/evaluation-options/CostBenefitAnalysis.
References
Howlett, W. and Coburn, T. (2019) Critical thinking | Podcast. [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/podcasts/critical-thinking#gref.
Lumenlearning.com. (2019) Rational Decision Making vs. Other Types of Decision Making | Principles of Management. [online] Available at: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wmopen-principlesofmanagement/chapter/rational-decision-making-vs-other-types-of-decision-making/ .
Mulder, P. (2019) Six Thinking Hats by Edward De Bono, a decision making tool | ToolsHero. [online] ToolsHero. Available at: https://www.toolshero.com/decision-making/six-thinking-hats-de-bono/.
Payal Sondhi (2018) 5 Important Guidelines to Increase HR Values In Your Organization. [online] Entrepreneur. Available at: https://www.entrepreneur.com/article/312696 .
Summer (2019) Understanding Of Micro And Macro Factors That Affect Your Business. [online] Mageplaza. Available at: https://www.mageplaza.com/blog/micro-and-macro-factors-affect-your-business.html.
Uzonwanne, F.C. (2016) Rational Model of Decision Making. Global Encyclopedia of Public Administration, Public Policy, and Governance, pp.1–6.
www.pagecentertraining.psu.edu. (2020). Ethical Theories. [online] Available at: https://www.pagecentertraining.psu.edu/public-relations-ethics/introduction-to-public-relations-ethics/lesson-1/ethical-theories/ .
Young, J. (2020) Evidence-based Practice for Effective Decision-Making | Factsheets. [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/analytics/evidence-based-practice-factsheet#gref .